
AI pioneer Innoplexus and phytopharmaceutical company DrD are partnering toRead More

AI pioneer Innoplexus and phytopharmaceutical company DrD are partnering toRead More
Jun 24
Apr 24

Innoplexus wins Horizon Interactive Gold Award for Curia App
Read MoreArtificial Intelligence garners more frontpage headlines every day. Artificial Intelligence, or AI, is the technology enabling machines to learn from experience and perform human-like tasks.
Ping-ponging between utopian and dystopian, opinions vary wildly regarding the current and future applications, or worse, implications, of artificial intelligence. Without the proper moorings, our minds tend to drift into Hollywood-manufactured waters, teeming with robot revolutions, autonomous cars, and very little understanding of how AI actually works.
This is mostly due to the fact that AI in itself is describing different technologies, which provide machines the ability to learn in an “intelligent” way.
In our coming series of blog posts, we hope to shed light on these technologies and clarify just what it is that makes artificial intelligence, well, intelligent.

Popular misconceptions tend to place AI on an island with robots and self-driving cars. However, this approach fails to recognize artificial intelligence’s major practical application; processing the vast amounts of data generated daily.
By strategically applying AI to certain processes, insight gathering and task automation occur at an otherwise unimaginable rate and scale.
Parsing through the mountains of data created by humans, AI systems perform intelligent searches, interpreting both text and images to discover patterns in complex data, and then act on those learnings.
Many of AI’s revolutionary technologies are common buzzwords, like “natural language processing,” “deep learning,” and “predictive analytics.” Cutting-edge technologies that enable computer systems to understand the meaning of human language, learn from experience, and make predictions, respectively.
Understanding AI jargon is the key to facilitating discussion about the real-world applications of this technology. The technologies are disruptive, revolutionizing the way humans interact with data and make decisions, and should be understood in basic terms by all of us.
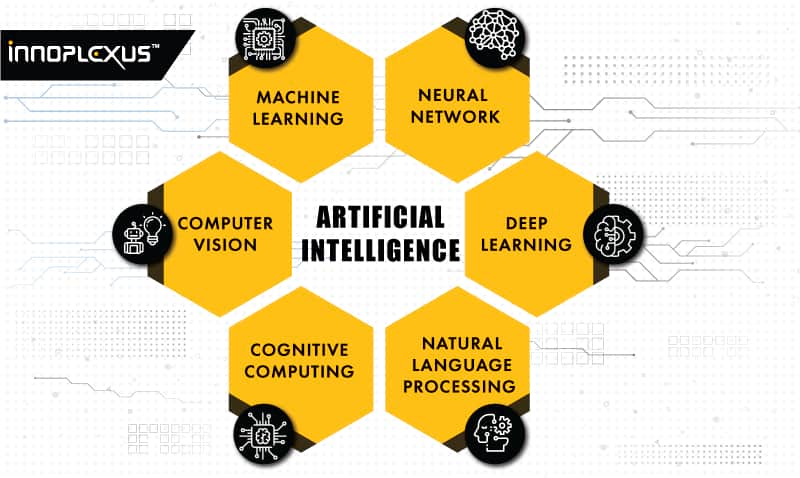

With the integration of Application Processing Interfaces or APIs, aspects of artificial intelligence can be plugged into existing software, augmenting its normal function with AI.
As we have learned, AI is describing a set of different technologies. Each of these technologies require detailed explanation. Staying up to date and understanding the differences of these technologies is a difficult task. Keep up with the latest changes and stay tuned for our upcoming posts.
Next, we will introduce Big Data and explore the applications of artificial intelligence solutions to structuring, connecting, and visualizing large data set to accelerate insight and empower decision-making.
The cost of developing a new drug roughly doubles every nine years (inflation-adjusted) aka Eroom’s law. As the volume of data…
There was a time when science depended on manual efforts by scientists and researchers. Then, came an avalanche of data…
Collaboration with key opinion leaders and influencers becomes crucial at various stages of the drug development chain. When a pharmaceutical…
Data are not the new gold – but the ability to put them together in a relevant and analyzable way…
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is gaining more attention in the pharma space these days. At one time evoking images from…
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming the pharmaceutical industry with extraordinary innovations that are automating processes at every stage of drug…
There is a lot of buzz these days about how artificial intelligence (AI) is going to disrupt the pharmaceutical industry….
Drug discovery plays a key role in the pharma and biotech industries. Discovering unmet needs, pinpointing the target, identifying the…
The pharmaceutical industry spends billions on R&D each year. Clinical trials require tremendous amounts of effort, from identifying sites and…
Training algorithms to identify and extract Life Sciences-specific data The English dictionary is full of words and definitions that can be…
The early 1970s introduced the world to the idea of computer vision, a promising technology automating tasks that would otherwise…
Summary: AI could potentially speed drug discovery and save time in rejecting treatments that are unlikely to yield worthwhile resultsAI has…